
This Codelab provides additional supporting documentation for installing Anypoint Flex Gateway as an ingress controller on a generic Kubernetes cluster (i.e., not cloud-platform specific). This Codelab aims to complement the documentation MuleSoft publishes and not replace it. Furthermore, we authored the content herein based on input, feedback, comment, questions, etc., we received from actual customers.
Flex Gateway Introduction
Flex Gateway is an ultrafast API gateway designed to manage and secure APIs running anywhere. It can secure both Mule and non-Mule APIs, and run anywhere — e.g., your cloud, on-premises, containerized environments, and hybrid
Flex Gateway supports two operating modes:
- In Local mode, Flex Gateway operates mostly disconnected from the Anypoint Control Plane. You manage Flex Gateway instances via locally stored declarative configuration files (YAML). In Local mode, network traffic is one-way, from Flex Gateway to the Anypoint Control Plane, and occurs:
- When registering and starting an instance for licensing and metering/billing purposes.
- When sending logs and metrics.
- In Connected mode, Flex Gateway is fully connected to the Anypoint control plane, which provides a single pane of glass for centralized management, observability, and security. In Connected mode, network traffic between Flex Gateway and the Anypoint Control Plane is bidirectional. For example, you can manage Flex Gateway instances and all APIs from the Anypoint Control Plane instead of maintaining YAML configuration files.
In this Codelab, we are using the default settings and Flex Gateway will run in connected mode.
Requirements
In this Codelab, you will need the following:
- An Anypoint Platform account,
- Docker Desktop on macOS or Windows, or Docker CE on Linux, and
- A Kubernetes cluster.
MuleSoft Relevant Documentation
This Codelab complements the following MuleSoft documentation:
Ensure you review and satisfy the following prerequisites before installing Anypoint Flex Gateway version 1.3 to a generic Kubernetes cluster.
Permission Requirements
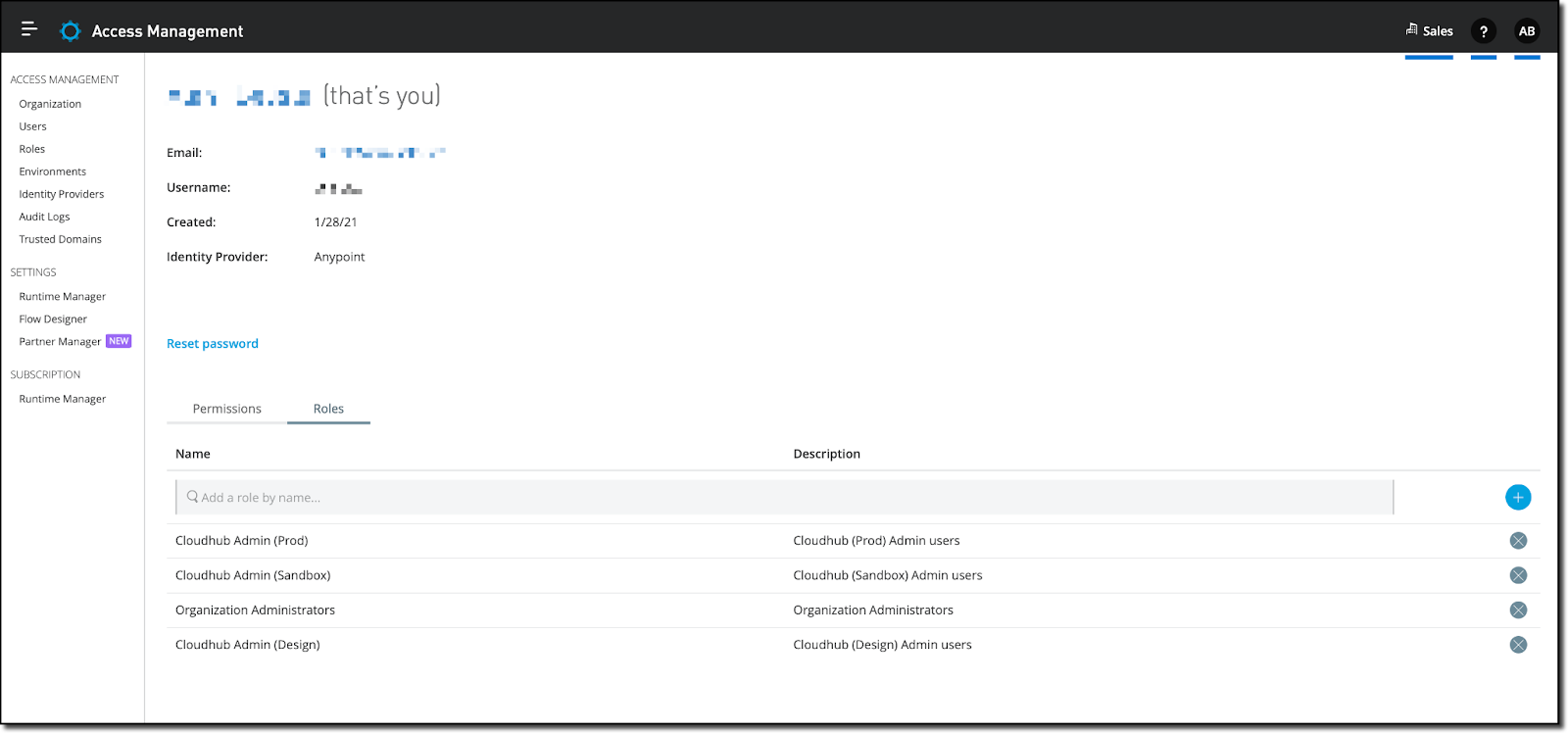
In Anypoint Platform, in Access Management more specifically, ensure your user account has the following permissions for Runtime Manager and the environment where you will install Flex Gateway:
- Manage Servers
- Read Servers
Software Requirements
Running Flex Gateway version 1.3 on Kubernetes requires the following:
- A minimum Kubernetes version of 1.21.
- Ingress v1 (stable), which requires specifying
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1as the API version in your configuration resources. - A minimum Helm version of 3.0.0.
Hardware Requirements
Flex Gateway requires the following minimum hardware configuration:
- CPU: 0.2 vCPU
- Memory: 200 MB
Ports, IPs, and Hostnames Allow list Requirements
Flex Gateway must communicate with the Anypoint Platform control plane. As relevant, ensure you add the following hostnames and ports to the allowlist.
US Control Plane
Host | Port | Description | Protocol |
anypoint.mulesoft.com | 443 | Required to connect with the control plane, push internal metrics, and download custom policy binaries | HTTPS |
arm-mcm2-service.kprod.msap.io | 443 | Required to communicate with the transport layer | mTLS |
logging.ingestion.us-east-1.prod.cloudhub.io | 443 | Required to send analytics data to the control plane | HTTPS |
metering.ingestion.us-east-1.prod.cloudhub.io | 443 | Required to send analytics data to the control plane | HTTPS |
monitoring.ingestion.us-east-1.prod.cloudhub.io | 443 | Required to send analytics data to the control plane | HTTPS |
exchange-files.anypoint.mulesoft.com | 443 | Required to download policies | HTTPS |
exchange2-asset-manager-kprod.s3.amazonaws.com | 443 | Required to download policies | HTTPS |
configuration-resolver.prod.cloudhub.io | 443 | Required to download policies | HTTPS |
EU Control Plane
Host | Port | Description | Protocol |
eu1.anypoint.mulesoft.com | 443 | Required to connect with the control plane, push internal metrics, and download custom policy binaries | HTTPS |
arm-mcm2-service.kprod-eu.msap.io | 443 | Required to communicate with the transport layer | mTLS |
logging.ingestion.eu-central-1.prod-eu.msap.io | 443 | Required to send analytics data to the control plane | HTTPS |
metering.ingestion.eu-central-1.prod-eu.msap.io | 443 | Required to send analytics data to the control plane | HTTPS |
monitoring.ingestion.eu-central-1.prod-eu.msap.io | 443 | Required to send analytics data to the control plane | HTTPS |
configuration-resolver.prod-eu.msap.io | 443 | Required to download policies | HTTPS |
exchange-files.eu1.anypoint.mulesoft.com | 443 | Required to download policies | HTTPS |
exchange2-asset-manager-kprod-eu.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com | 443 | Required to download policies | HTTPS |
When adding Flex Gateway to Kubernetes, the recommended approach is to follow the generic instructions Anypoint Runtime Manager provides. More specifically, the organization id and registration token are prepopulated in step 2 (Register your gateway) and are specific to 1) the business group and 2) the environment selected. For example, we selected the Sales business group and the Prod environment in the following screen capture, and the prepopulated values reflect those selections.
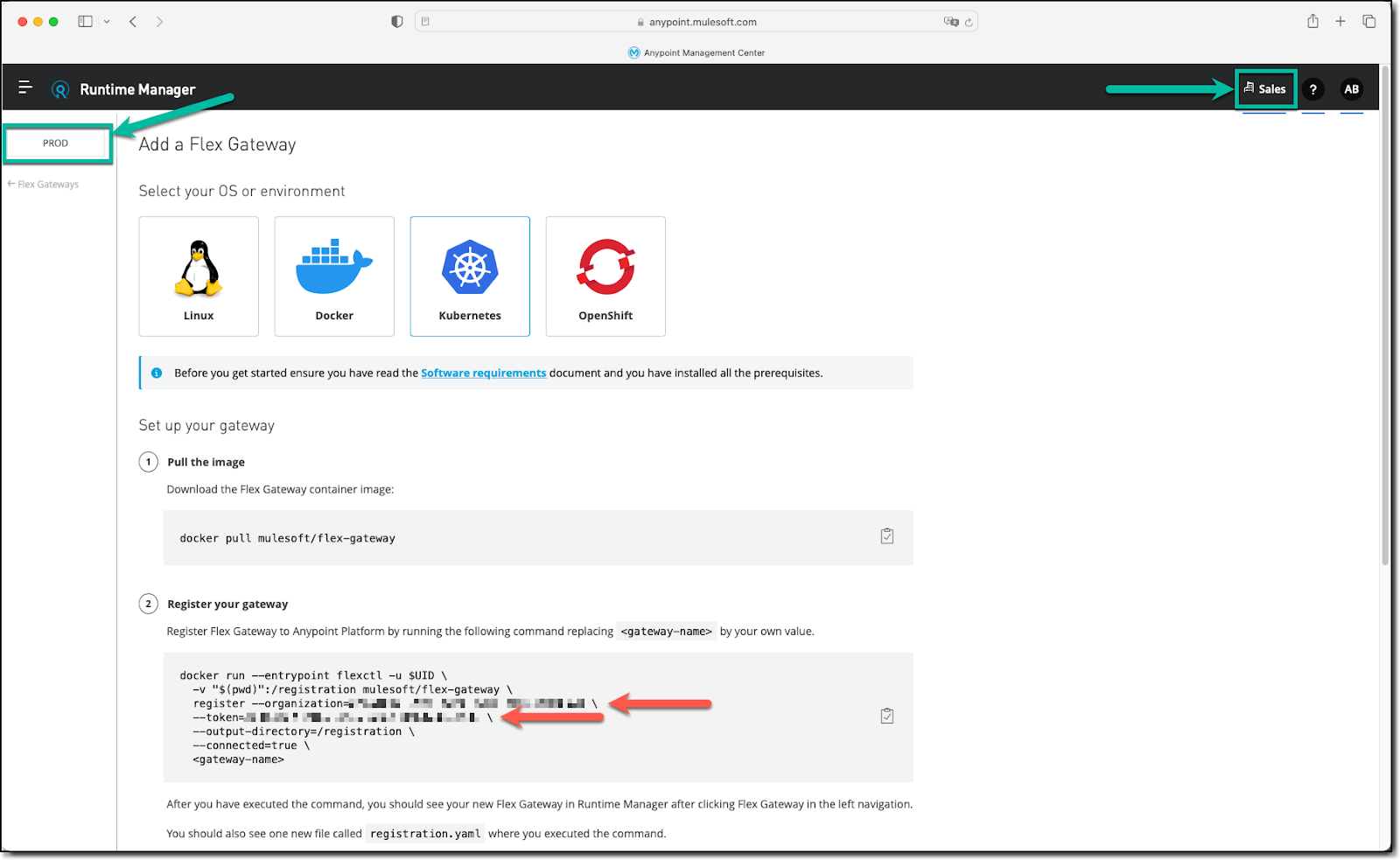
In this Codelab, we review those generic instructions but more importantly, we add additional details to complement them.
Step 1 of the Anypoint Runtime Manager generic instructions consists of downloading the Docker image of Flex Gateway from Docker Hub, which we use to register a new instance of Flex Gateway in the next step. The generic instructions imply completing this step on our computer using Docker Desktop on macOS or Windows, or Docker CE on Linux, as examples.
- Ensure Docker is running on your computer.
- Open a command line window (Windows) or a terminal (Linux or Mac), and run the following command:
docker pull mulesoft/flex-gateway
Step 2 of the Anypoint Runtime Manager generic instructions involves running the Docker image to register a Flex Gateway instance with the Anypoint Platform control plane. To do so, we suggest leveraging the command generated in Anypoint Runtime Manager, as it is prepopulated based on the business group and environment selected.
- First, open a web browser and log in to the Anypoint Platform (https://anypoint.mulesoft.com).
- On the landing page, select Runtime Manager in the Management Center section on the right.
- In Runtime Manager, if applicable, first select the appropriate business group (top right corner) and then the correct environment (top left corner).
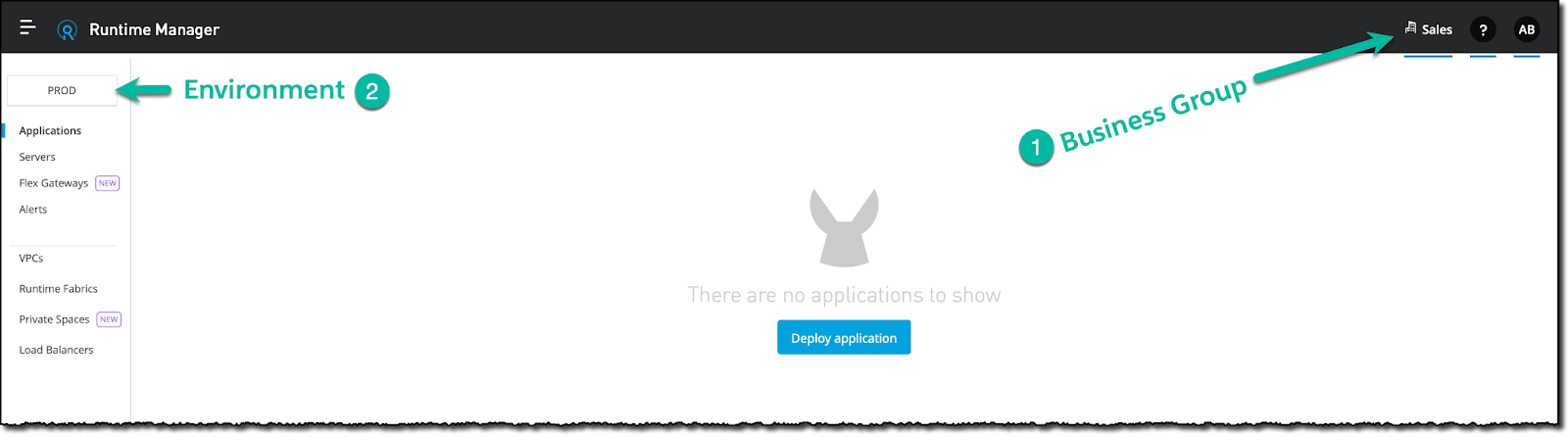
- Next, select the Flex Gateways option in the left menu
- On the Flex Gateways page, click the Add Gateway button and click the Kubernetes logo.
- Locate step 2 (Register your gateway) in the high-level instructions displayed and and notice the command. As stated before, this command is prepopulated and require one minor edit. More specifically:
- The
--organizationoption represents the organization id of the business group selected, and - The
--tokenoption represents the registration token specific to the environment selected.
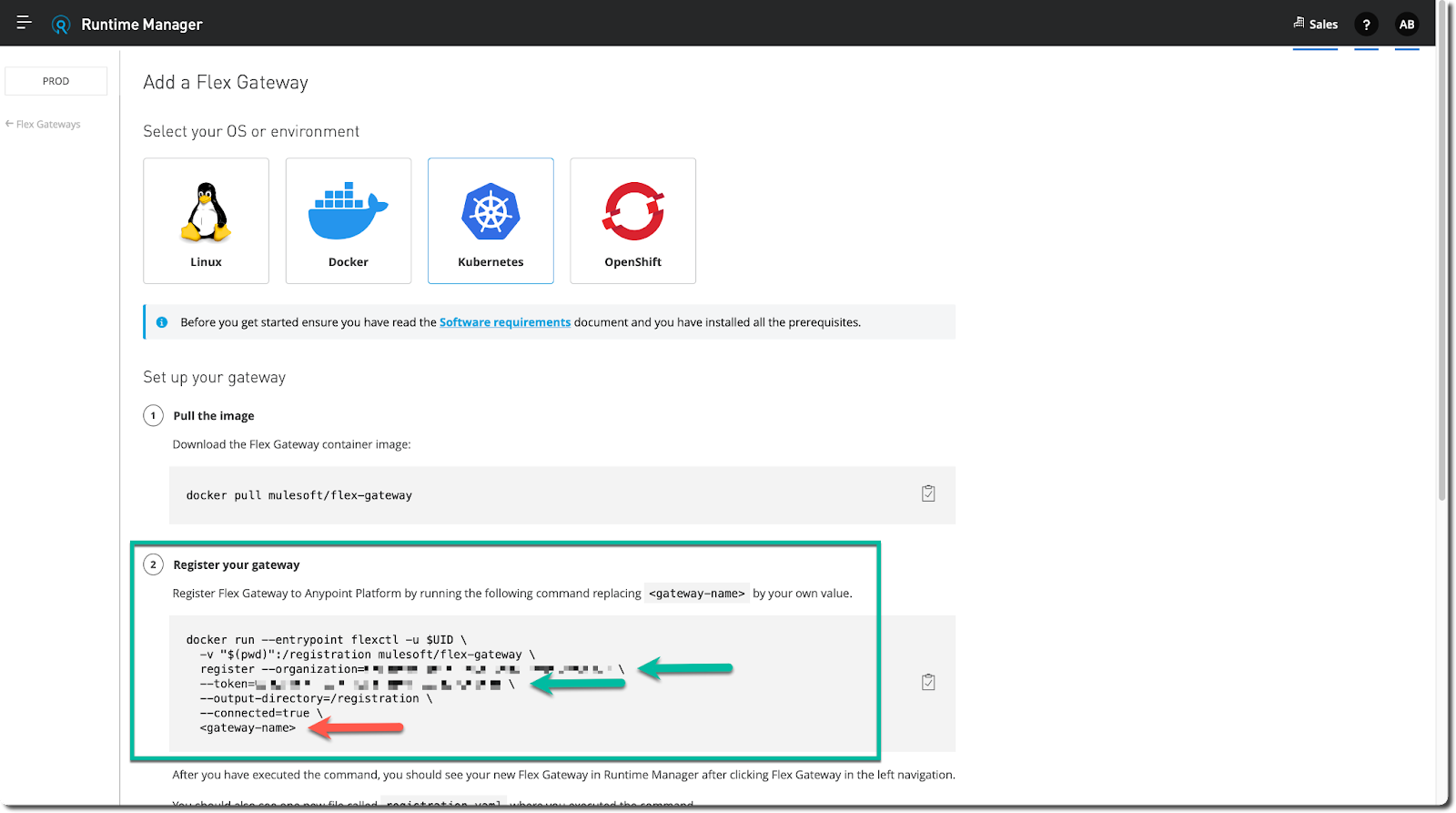
- Copy the entire
docker runcommand and paste it into a text editor to alter it before running it. As the changes are minor, you can paste it to the command line window (Windows) or the terminal (Linux or Mac) you opened in the previous step, but do not run the command yet. We pasted the generic command here for convenience.
docker run --entrypoint flexctl -u $UID \ -v "$(pwd)":/registration mulesoft/flex-gateway \ register --organization=<organization-id> \ --token=<registration-token> \ --output-directory=/registration \ --connected=true \ <gateway-name>
- Edit the
docker runcommand and replace the placeholder with the name of your Flex Gateway instance. - Optionally, add the
--rmflag before the--entrypointflag (i.e.,docker run --rm --entrypoint...) to dispose of the container automatically once the registration completes, as it is no longer required. - Finally, paste
docker runcommand to the command line window (Windows) or the terminal (Linux or Mac) and execute it.
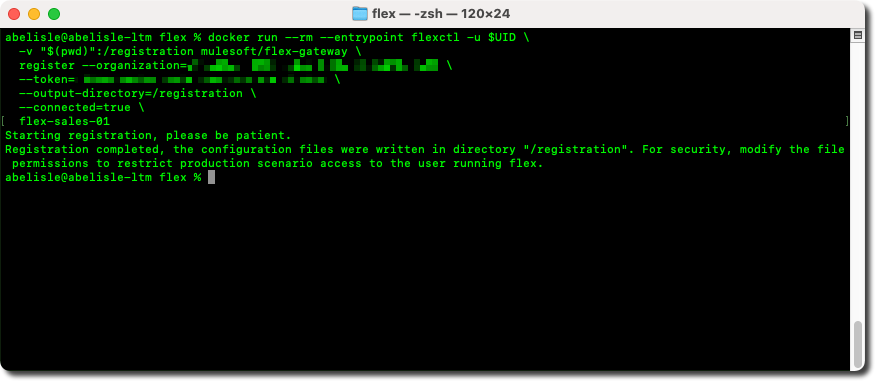
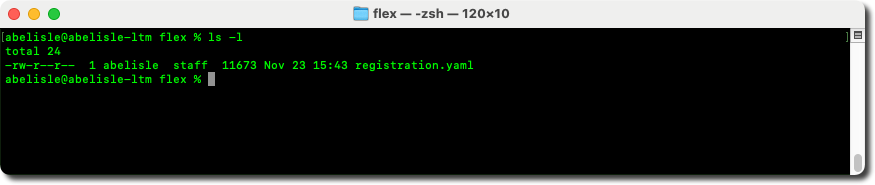
- This command registers a new instance of Flex Gateway to the Anypoint Platform control plane, and when successful, it creates a registration file in the current directory named
registration.yaml.
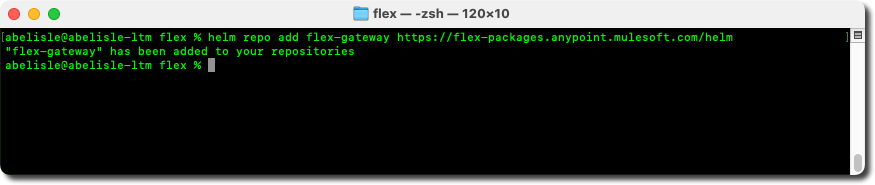
Step 3 of the Anypoint Runtime Manager generic instructions involves connecting to the Kubernetes cluster to add the Helm chart repository for Flex Gateway.
- Connect to your Kubernetes cluster using the command-line interface, for example.
- First, add the Helm chart repository for Flex Gateway using the following command:
helm repo add flex-gateway https://flex-packages.anypoint.mulesoft.com/helm
- Then, update information locally on available charts from the newly added Flex Gateway chart repository using the following command:
helm repo update
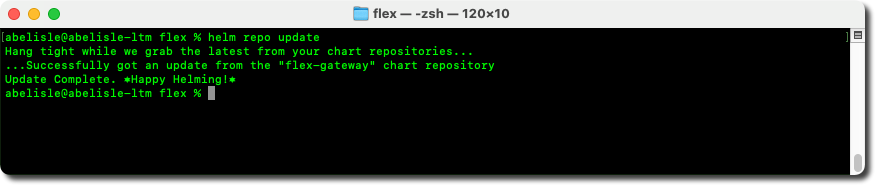
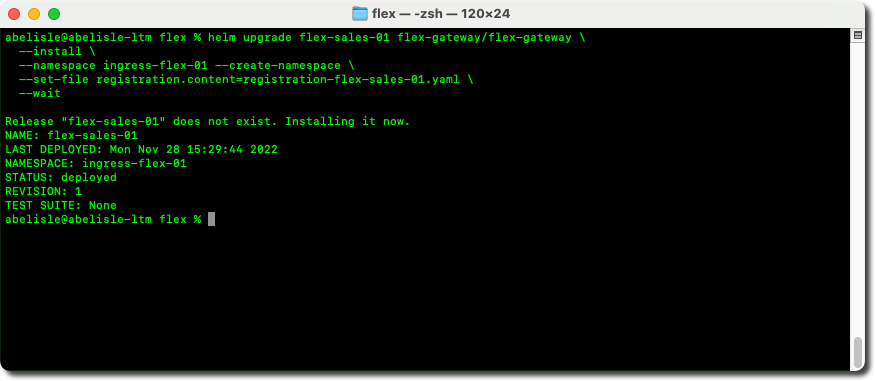
Step 4 of the Anypoint Runtime Manager generic instructions consists of deploying a Flex Gateway instance to the Kubernetes cluster using Helm and the registration file from step 2.
- If you disconnected, reconnect to your Kubernetes cluster using the command-line interface, for example.
- Copy the following command, adjust and update it as needed.
helm upgrade <release-name> flex-gateway/flex-gateway \ --install \ --namespace <namespace-name> --create-namespace \ --set-file registration.content=<registration-file-name> \ --wait
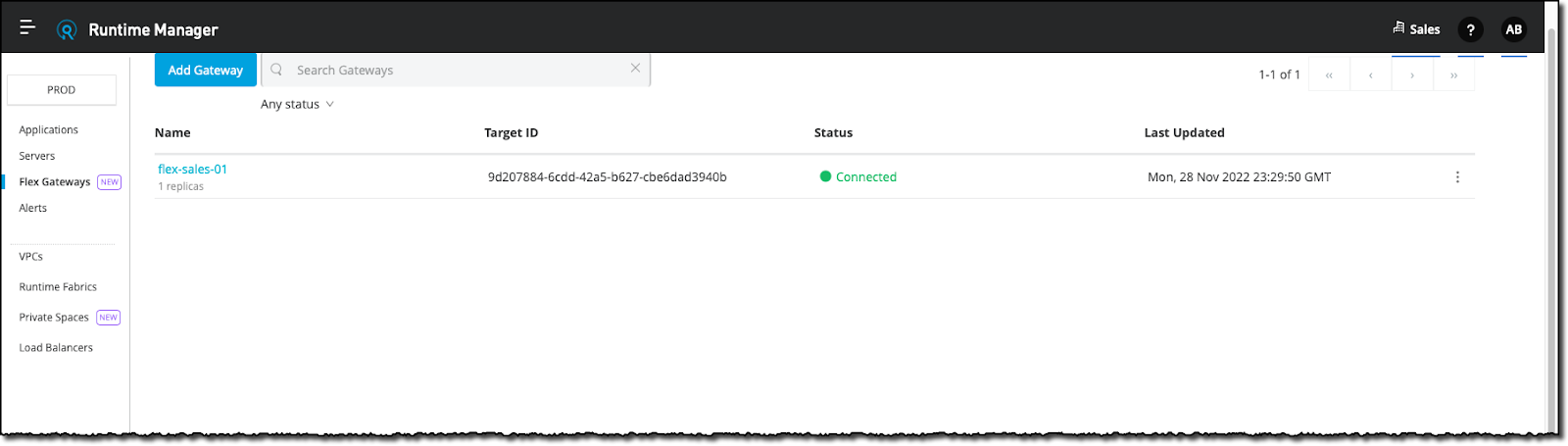
Finally, step 5 of the Anypoint Runtime Manager generic instructions consists of verifying that the Flex Gateway instance connected successfully to the Anypoint Platform control plane.
- If you close it, open a web browser and log in to the Anypoint Platform (https://anypoint.mulesoft.com).
- On the landing page, select Runtime Manager in the Management Center section on the right.
- In Runtime Manager, if applicable, first select the appropriate business group (top right corner) and then the correct environment (top left corner).

- Next, select the Flex Gateways option in the left menu
- You should now see your Flex Gateway instance connected to the Anypoint Platform control plane.
In this Codelab, you install Anypoint Flex Gateway as an ingress controller on a generic Kubernetes cluster (i.e., not cloud-platform specific). This Codelab uses the default settings, which means that your Flex Gateway instance runs in connected mode.